- Renewal of expired RHCE certification from February 2006 (100% exam pass mark) #804006064719004
- Renewed RHCE #160-204-699
- https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/rh299-rhce-certification-lab
- Monday 26th September 2016 - Thursday 29th September 2016 inclusive.
- EX300 (RHCE) exam on Friday 30th September 2016 @ 8:45am.
- http://content.example.com/rhel7.0/x86_64/dvd
Don't forget to use the power of updatedb and then locate, mandb and man -K, and yum search all SOMETHING. Also look for examples under /usr/share/doc/, grep -ri "SOMETHING" /usr/share/doc/. May the force be with you.
| Host | IP | Description |
|---|---|---|
classroom.example.com | 172.25.N.254 | |
content.example.com | 172.15.254.254 | |
foundationN.itl.example.com | Physical laptop / hypervisor | |
desktopN.example.com | Desktop test VM | |
exampleN.example.com | Server test VM |
| Username | Password | Description |
|---|---|---|
kiosk | redhat | Physical laptop login |
root | redhat | VM root user |
student | student | VM non-privileged user |
Custom course commands:
lab- Start pre-defined lab scenariorht-vmctl- Administer test virtual machines
Day 1
Course textbook 1, chapter 9.
Course textbook 2, pages 63-70.
lsinitrd- wrapper around initial ramdisk image (looks for magic strings inside the image file to seperate the first cpio archive from the second part of the image).
systemd
systemctlcommands referencing object or units that do not specify the '.type' suffix, are assumed to service objects, and are automatically suffixed with.service.- Targets are analagous to old
init"runlevels".telinitis analagous tosystemctl isolate foo-unit.target- Useful targets are:
multi-user.target,rescue.targetandemergency.target(similar torescue.target, but gives you the shell after the root filesystem pivot has happened).
- Kernel argument
systemd.unit=mytarget.targetsets the systemd target.systemctl get-defaultandsystemctl set-default <TARGET>can be used to change the default target.
systemctl enable debug-shell.service- Provides a password-less root shell on VTY9 (Ctrl-Alt-F9) to debug the systemd boot process at boot time.
systelctl list-jobs
- Additional useful arguments are:
is-enabled,is-active,list-units,list-unit-files(enabled, loaded or not),--output=json,--no-legend,--no-pager,show(machine readable version ofstatus).
Grub2 & Dracut
- Kernel argument
rd.breakis analagous to the oldSorsinglekernel argument for single usermode, in that it will dump you to a shell inside the initial ramdisk image (Dracut) environment.mount -o remount,rw /sysroot- Target root filesystem is mounted read-only on/sysrootbefore pivot.
- Kernel argument
selinux=0andenforcing=0will overload/etc/sysconfig/selinuxvalues at boot. touch /.autorelabelwill force default SELinux labels to be restored to core files at boot (necessary if you clobber SELinux labels by changing the root password from inside Dracut for example, as Dracut runs without SELinux).
journald
To persist journald log databases between reboots:
mkdir /var/log/journal \
&& chown root:system-journal /var/log/journal \
&& chmod 2755 /var/log/journal \
&& systemctl restart systemd-journal.servicefirewalld
firewald.service- systemd object / unit service name.firewall-configfirewall-cmd- Remember to use the
--permanentargument to persist the configuration change to disk, and then usefirewall-cmd reloadto apply it, otherwise the change will be made to the current running configuration only.
- Remember to use the
firewall-offline-cmd/lib/firewalld/(and by extension due to the/usr/symlink,/usr/lib/firewalld/)/etc/firewalld/
Day 2
yum historyyum history undo NUMyum history redo NUMyum provides "*/foocmd"
Network Filesystems
Workbook 2, chapter 7 (providing file-based storage), page 173
- Protecting NFS Exports - page 181
- Make sure you have the packages installed before you run
authconfig, otherwise it may configure a next-best alternative and not do what you think it should do when you reconfigure withauthconfigafter the fact. yum install sssd auhconfig-gtk krb5-workstation autofsauthconfig-gtkorauthconfig-tui- Domain is
example.com - Realm name is
EXAMPLE.COM - KDC admin and server name is
classroom.example.com - CA certificate is located on http://classroom.example.com/pub/example-ca.crt
- LDAP user's home on NFS server
classroom.example.com:/home/guests - LDAP user's name is ldapuserX where X is your station number
- Make sure you have the packages installed before you run
# /etc/auto.master
/home/guests /etc/auto.ldapguests
# /etc/auto.ldapguests
* -fstype=nfs,rw,async,hard,intr classroom.example.com:/home/guests/&- Performing a Multi-User SMB Mount - page 202
yum -y install cifs-utilscifscreds add REMOTE_HOSTNAME- Assumes the current local usernamemount -o multiuser,sec=ntlmspp,username=MYUSERNAME //serverX/myshare /mnt/multiuser
- Filesystem ACLs
getfacl,setfacl,chacl
Firewalld Direct Rules
Workbook 2, chapter 3 (network port security), page 71.
- Direct are rules that are specified with
--directargument, allowing more flexibilty to create the underlaying iptables rules.- Direct rules are handled first, before any other rules in any firewalld zones.
- Direct rules still behave the same with regards to the
firewalld-cmd --permanentargument.
Firewalld Rich Rules
- Rich rules are similar to direct rules, specified with
--add-rich-rule, but are applied to a specific firewalld zone (or the default zone if no zone is specified by with--zone=ZONEargument.- Rich rules still behave the same with regards to the
firewalld-cmd --permanentargument.
- Rich rules still behave the same with regards to the
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=dmz --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.N.10/32 service name=http log level=notice prefix="NEW HTTP " limit value="3/s" accept'
Firewalld Port Masquerading & Forwarding
The SNAT target requires you to give it an IP address to apply to all the outgoing packets. The MASQUERADE target lets you give it an interface, and whatever address is on that interface is the address that is applied to all the outgoing packets. In addition, with SNAT, the kernel's connection tracking keeps track of all the connections when the interface is taken down and brought back up; the same is not true for the MASQUERADE target.
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=ZONE --add-masquerade- Will masquerate any packets sent to the firewall from clients defined in the sources for that zone (both interfaces and subnets) that are not addressed to the firewall host itself.- Using
--add-rich-rulegives you more control over what client source addresses will me masqueraded:firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=ZONE --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.0.0/24 masquerade'
- Using
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=ZONE --add-forward-port="port=ORIGINAL_PORTNUMBER:proto=PROTO[:toport=NEWDEST_PORTNUMBER][:toaddr=NEWDEST_IP]- Forwarding may also use
--add-rich-rulelike so:firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=ZONE --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.0.0/26 forward-port port=80 protocol=tcp to-port=8080'
- Forwarding may also use
SELinux
Workbook 2, chapter 3 (network port security), page 81.
- Configure via GUI
system-config-selinux(from thepolicycoreutils-gui). - Check, disable and enable temporarily:
getenforce,setenforce 0andsetenforce 1. - Permanent state configuration in
/etc/selinux/configor/etc/sysconfig/selinux. - See SELinux status with
sestatuscommand. semanage fcontext -l- List file context definitionssemanage port -l- List port context definitions- Find SELinux violations in
/var/log/messages.- Use
sealertto find out the details. sealert -a /var/log/audit/audit.log- https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Security-Enhanced_Linux/sect-Security-Enhanced_Linux-Fixing_Problems-sealert_Messages.html
- Use
- Example to add a port to an SELinux type/label
semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 8089 - Man pages:
semanage(8),semanage-port(8),system-config-linux(8). yum -y install selinx-policy-develfor a large number of SELinux port type/label definitions.
Workbook 1, chapter 5 (SELinux permissions), page 111.
- SELinux context has 4 parts; user:role:type:category.
[root@cp1 ~]# ls -Z anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-------. root root system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 anaconda-ks.cfggetsebool -aandsetseboolsetsebool BOOLEAN onsetsebool -P BOOLEAN on- persist change through rebootssemanage boolean -l
chconandrestoreconsemanage fcontext -a -t admin_home_t '/common(/.*)?'- sets the default type context for/commonand all files and sub-directories to beadmin_home_trunconwill run a process under a specific context.
MariaDB
Workbook 2, page 226.
yum groupinstall mariadb mariadb-clientmysql_secure_installationecho -e "[mysqld]\nskip-networking=1\n" > /etc/my.cnf.d/skip-networking.cnfhelp create user,help grant...flush privileges;flush tables with read lock; unlock tables;
Day 3
iSCSI
Workbook 2, chapter 6 (providing remote block storage), page 145.
A quick Google yields https://www.thomas-krenn.com/en/wiki/ISCSI_Basics and man iscsiadm.
- Target iSCSI server
- Initiator iSCSI client
- Node server
- iQN
iqn.YYYY-MM.com.reversed.server.fqdn:optional_name - ACL uses iQN
- LUN - Logical Unit Number
- Portal
172.25.0.11eth0eth1eth3 - Discovery
iscsiadm -m discovery -t send_targets -p 10.10.10.10@salikov example
- Login
- iSCSI still uses CDB (Command Descriptor Block) command set originally defined by the original SCSI standards.
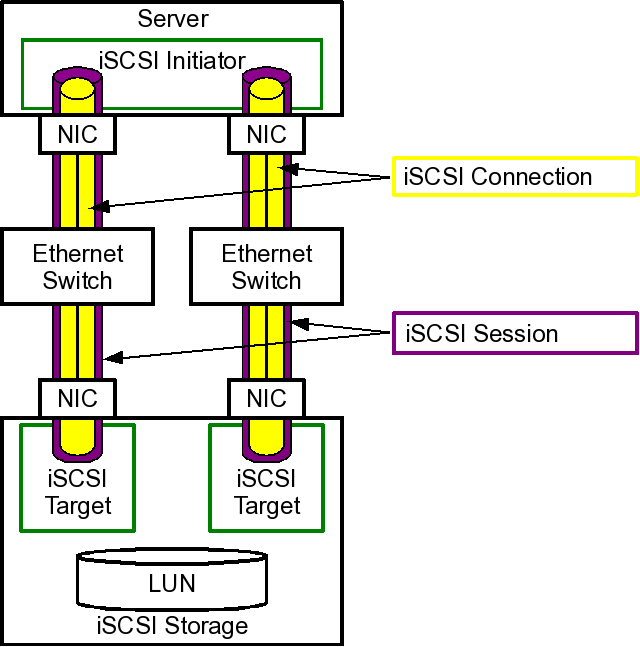
iSCSI Server
yum install targetcli
[root@server9:~] $ targetcli
/> lsfirewall-cmd --add-port=3260/tcpfirewall-cmd --add-port=3260/tcp --permanentsystemctl endable targetsystemctl start target
iSCSI Client
yum install iscsi-initiator-utilsecho "InitiatorName=iqn.2016-09.com.example.desktop9:optional_name" > /etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi- systemctl restart iscsid
- only necessary if you changed the initiator name after doing a scan ** systemctl restart iscsi
- systemctl restart iscsid
iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p 172.25.N.11- Caches persistently into
/var/lib/iscsi/nodes/
- Caches persistently into
iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2016-09.com.example.server9:optional_name -p 172.25.N.11 -lto login to tagret iQN at portal addressiscsiadm -m sessionto show establisted iSCSI sessionslsblk -o +UUIDto show the new block device (check under/sys/block/)- Partition and format the new block device.
- Add filesystem using UUID to
/etc/fstab. - You can logout and remove the iSCSI disk permanently if you wish using
iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2016-09.com.example.server9:optional_name -p 172.25.N.11 -o delete
NetworkMangler
Workbook 2, chapter 1 (managing ipv6 networking), page 1.
- Relies on
NetworkManagersystemd service. nmcli,nmtui,nm*/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-*/etc/NetworkManagerhostnamectl
Postfix
Workbook 2, chapter 5 (configuring email transmission), page 134.
postconf -e "local_transmission=error: local delivery disabled"postconf -e "relayhost=smtpX.example.com"postconf -e "inet_interfaces=loopback-only"postconf -e "mynetworks="127.0.0.1/8 [::1]/128"postconf -e "myorigin=desktopX.example.com"postconf -e "mydestination="systemctl restart postfix
Day 4
Network Bonding
A comparisson of network teaming vs network bonding in Linux https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/Networking_Guide/sec-Comparison_of_Network_Teaming_to_Bonding.html.
teamdctl INTERFACE stateteamnlnmcli connection modify team0 team.config '{"runner":{"name":"activebackup"}}'nmcli connection show team0 | grep0 teamnmcli connection down team0nmcli connection up team0/usr/share/doc/teamd-*/
Network Bridges
brctlnmcli con add con-name br0 ifname br0 type bridge
NFS
yum install -y krb5-workstation sssd authconfig-gtk nfs-utils- Install Kerberos
/etc/krb5.keytabfile sec=krb5pchronyc sourcessystemctl enable nfs-serversystemctl enable nfs-secure-serversystemctl enable nfs-secure- client onlyfirewall-cmd --add-service=nfs --permanentfirewall-cmd --add-service=rpc-bind --permanentfirewall-cmd --add-service=mountd --permanentfirewall-cmd --reloadshowmount HOST --exportsexportfs -avr
Samba
yum install samba samba-client cifs-utilsgetenforcels -Z /your/share/semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t '/your/share(/.*)?'restorecon -Rv /your/sharels -Z /your/share/systemctl enable smb.servicesystemctl restart smb.serviceuseradd -G sysusers -s /usr/sbin/nologin bobsmbpasswd -a susanpdbedit -Lto list the samba userstestparmto test the samba configurationfirewall-cmd --add-service=samba --permanentfirewall-cmd --reload
echo “username=user9″ > /root/user9.txt
echo “password=userpass” >> /root/user9.txt
mount -o sec=ntlmssp,multiuser,credentials=/root/user9.txt \
//server9/myshare /smbshare
cifscreds add server9